There are many Gum Disease causes, including a poor diet, hormonal imbalances, and genetics. People with certain conditions may be at increased risk of gum disease. Some medications, such as chemotherapy, can increase the risk of developing periodontal disease. Other causes include diabetes, AIDS, and cancer treatments. While there is no one surefire cause of gum disease, the early detection and treatment of gum disease can save your teeth.
Inflammatory diseases can occur in the gums, and can be caused by certain medicines. These include antihistamines, antidepressants, and drugs for hypertension. Other factors can cause gum disease, including certain genetics and hormonal changes. For people with diabetes, it’s critical to follow the instructions of their physician and undergo regular dental visits. If you’re suffering from periodontal disease, it’s important to visit a dentist as soon as possible.
Some people are genetically predisposed to gum disease. There are a few diseases that can weaken the immune system and make it more vulnerable to infections. Infections in the mouth can result in an abscess, which is painful and requires immediate treatment. In severe cases, infections can spread to the jaw bone, and may eventually result in tooth loss. Some people are more susceptible to gum disease than others. Some people simply have a poor oral hygiene routine.
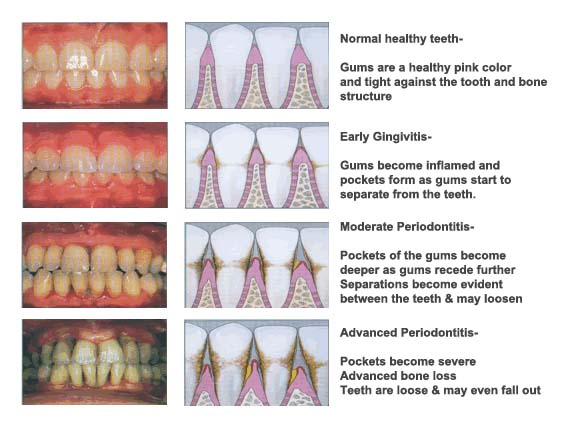
There are several different causes of gum inflammation. Some are preventable and some are permanent. Gum inflammation is the most common symptom of gum disease. Although the gums are often red and swollen, other symptoms may include bleeding and soreness. They may also bleed when you brush or floss your teeth. These symptoms are signs of a more serious problem. You should visit your dentist and regularly visit a health website Tonerin to find out what is causing your gum disease.
If you have gum disease, you should visit your dentist. These conditions can increase your risk of gum disease. You should know your health history and be careful about how you use tobacco. Some of these medications may increase your risk of developing periodontal disease. If you have diabetes, it is best to avoid smoking. This can affect your immune system and negatively impact your oral health. It is important to visit your dentist regularly to monitor your oral health.
Gum disease is caused by bacteria that live in the mouth. These bacteria feed on the sugars in your food and produce toxins. These toxins can cause your gums to swell and bleed. In severe cases, bacteria can damage the bones and fibers that support teeth. In severe cases, you may need to have teeth removed to stop the infection. These symptoms are not only painful, but can also affect your oral health.
In addition to plaque, bacteria can also cause gum disease. They feed on the sugars in the food you eat and produce toxic chemicals and poisons. These toxins can irritate your gums and cause them to bleed and become swollen. These toxins can also cause periodontitis. The infection can spread to nearby teeth and jaw bone. If left untreated, it can even lead to tooth loss. Besides plaque and bacteria, other causes of periodontal disease include genetics and tobacco use.
The most common symptom of gum disease is bleeding while brushing and flossing. A person with a bleeding gum is a good candidate for a periodontal infection. In some cases, the bleeding can be so severe that a tooth may need to be removed. When it occurs, the infection can lead to an abscess and a painful tooth root. Sometimes, the infection will spread to the jaw bone, causing a bleed, and in such a case, the infection may become serious.
While gum disease may not have any symptoms, it can be a sign of more serious problems. Infections in the mouth can cause a tooth to fall out, so it is important to be aware of what you’re taking. Some of the most common medications can affect oral health. Patients who are taking antibiotics should inform their dentist of any medications they take. Other medications, such as birth control pills, may be at greater risk of developing periodontitis.
